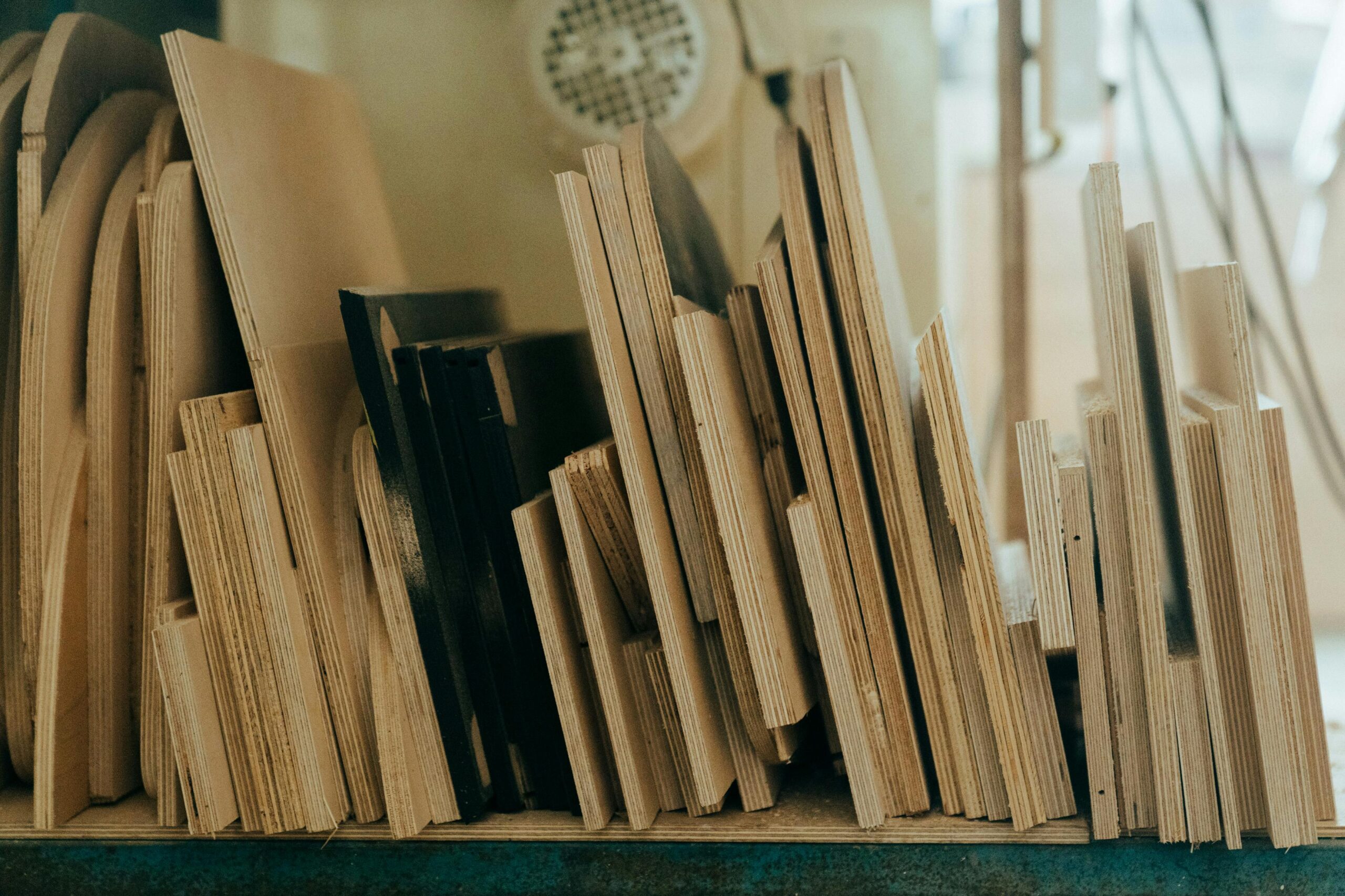
When it comes to choosing between MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) and plywood for your woodworking or home improvement projects, understanding their differences and advantages is crucial. Both materials have their own unique properties, making them suitable for different applications. Here’s a closer look at each to help you decide which is better for your needs.
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard)
MDF is an engineered wood product made from wood fibers, wax, and resin, compressed under high pressure and heat. It is known for its smooth surface and uniform density. Here are some key benefits of MDF:
- Smooth Surface: MDF has a very smooth and consistent surface, making it ideal for painting and veneering.
- Cost-Effective: It is generally less expensive than plywood.
- Workability: Easy to cut, shape, and drill without splintering, making it a favorite for detailed work.
However, MDF also has some drawbacks:
- Moisture Sensitivity: MDF is not water-resistant and can swell or warp when exposed to moisture.
- Weight: It is heavier than plywood, which can make handling and installation more challenging.
- Strength: MDF is not as strong or durable as plywood, making it less suitable for load-bearing applications.
Plywood
Plywood is made by gluing together thin layers of wood veneer, with the grain of each layer running in different directions. This cross-graining gives plywood its strength and durability. Here are some key advantages of plywood:
- Strength and Durability: Plywood is stronger and more durable than MDF, making it suitable for structural applications.
- Moisture Resistance: Higher grades of plywood are more resistant to moisture, making them a better choice for areas prone to humidity.
- Versatility: Plywood comes in various grades, thicknesses, and types, allowing for a wide range of uses from construction to furniture making.
However, plywood has its own set of disadvantages:
- Cost: High-quality plywood can be more expensive than MDF.
- Surface: Plywood surfaces can be rough and may require additional finishing work.
- Workability: Plywood can splinter and is more challenging to cut smoothly compared to MDF.
Conclusion
Choosing between MDF and plywood depends largely on the specific requirements of your project. For applications requiring strength and durability, such as cabinetry or structural elements, plywood is the better choice. For projects where a smooth finish and cost-effectiveness are priorities, MDF is a suitable option. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision and ensure the success of your project.